Download
Step 1. Add the JitPack repository to your build file
Add it in your root settings.gradle at the end of repositories:
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS)
repositories {
mavenCentral()
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
}Add it in your settings.gradle.kts at the end of repositories:
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS)
repositories {
mavenCentral()
maven { url = uri("https://jitpack.io") }
}
}Add to pom.xml
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jitpack.io</id>
<url>https://jitpack.io</url>
</repository>
</repositories>Add it in your build.sbt at the end of resolvers:
resolvers += "jitpack" at "https://jitpack.io"
Add it in your project.clj at the end of repositories:
:repositories [["jitpack" "https://jitpack.io"]]
Step 2. Add the dependency
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.dangdangdotcom:sharding-jdbc:5.5.2'
} dependencies {
implementation("com.github.dangdangdotcom:sharding-jdbc:5.5.2")
} <dependency>
<groupId>com.github.dangdangdotcom</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.5.2</version>
</dependency>
libraryDependencies += "com.github.dangdangdotcom" % "sharding-jdbc" % "5.5.2"
:dependencies [[com.github.dangdangdotcom/sharding-jdbc "5.5.2"]]
Readme
Apache ShardingSphere - Enterprise Distributed Database Ecosystem
Building the standards and ecosystem on top of heterogeneous databases, empowering enterprise data architecture transformation
Official Website: https://shardingsphere.apache.org/
<table style="width:100%"> <tr> <th> <a href="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map?activity=stars&repo_id=49876476" target="_blank" style="display: block" align="center"> <picture> <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map/thumbnail.png?activity=stars&repo_id=49876476&image_size=auto&color_scheme=dark" width="721" height="auto"> <img alt="Star Geographical Distribution of apache/shardingsphere" src="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map/thumbnail.png?activity=stars&repo_id=49876476&image_size=auto&color_scheme=light" width="721" height="auto"> </picture> </a> </th> <th> <a href="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map?activity=pull-request-creators&repo_id=49876476" target="_blank" style="display: block" align="center"> <picture> <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map/thumbnail.png?activity=pull-request-creators&repo_id=49876476&image_size=auto&color_scheme=dark" width="721" height="auto"> <img alt="Pull Request Creator Geographical Distribution of apache/shardingsphere" src="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map/thumbnail.png?activity=pull-request-creators&repo_id=49876476&image_size=auto&color_scheme=light" width="721" height="auto"> </picture> </a> </th> <th> <a href="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map?activity=issue-creators&repo_id=49876476" target="_blank" style="display: block" align="center"> <picture> <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map/thumbnail.png?activity=issue-creators&repo_id=49876476&image_size=auto&color_scheme=dark" width="721" height="auto"> <img alt="Issue Creator Geographical Distribution of apache/shardingsphere" src="https://next.ossinsight.io/widgets/official/analyze-repo-stars-map/thumbnail.png?activity=issue-creators&repo_id=49876476&image_size=auto&color_scheme=light" width="721" height="auto"> </picture> </a> </th> </tr> </table>OVERVIEW
<hr>Apache ShardingSphere is positioned as Database Plus, a standard and ecosystem built on top of heterogeneous databases. As an operating system layer above databases, ShardingSphere does not create new databases but focuses on maximizing the computing capabilities of existing databases, providing unified data access and enhanced computing capabilities.
Database Plus Core Concept: By building a standardized and scalable enhancement layer above databases, it makes heterogeneous databases as simple to use as a single database, providing unified governance capabilities and distributed computing capabilities for enterprise data architectures.
Connect, Enhance, and Pluggable are the three core pillars of Apache ShardingSphere:
-
Connect: Building database upper-layer standards, quickly connecting applications with multi-modal heterogeneous databases through flexible adaptation of database protocols, SQL dialects, and storage formats, providing unified data access experience;
-
Enhance: As a database computing enhancement engine, transparently providing enterprise-grade capabilities including distributed computing (data sharding, readwrite-splitting, SQL federation), data security (encryption, masking, audit), traffic control (circuit breaker, rate limiting), and observability (monitoring, tracing, analysis);
-
Pluggable: Adopting a micro-kernel + 3-layer pluggable architecture to achieve complete decoupling of kernel, functional components, and ecosystem integration. Developers can flexibly customize unique data architecture solutions that meet enterprise needs, just like building with LEGO blocks.
Differentiation Advantages:
- vs Distributed Databases: More lightweight, protecting existing investments, avoiding vendor lock-in
- vs Traditional Middleware: Richer features, more complete ecosystem, more flexible architecture
- vs Cloud Vendor Solutions: Support multi-cloud deployment, avoid technology binding, autonomous and controllable
ShardingSphere became an Apache Top-Level Project on April 16, 2020, and has been adopted by 19,000+ projects worldwide.
DUAL-ACCESS ARCHITECTURE DESIGN
<hr>ShardingSphere adopts a unique dual-access architecture design, providing two access ends - JDBC and Proxy - that can be deployed independently or in hybrid deployment, meeting diverse requirements for different scenarios.
ShardingSphere-JDBC: Lightweight Access End
Positioning: Lightweight Java framework, enhanced JDBC driver
Core Features:
- Client-side direct connection: Shares resources with applications, decentralized architecture
- High performance, low overhead: Direct database connection with minimal performance loss
- Complete compatibility: Compatible with all ORM frameworks (MyBatis, JPA, Hibernate, etc.)
- Zero additional deployment: Provided as JAR package, no independent deployment and dependencies required
Use Cases: High-performance Java applications, integrated deployment with business applications, pursuing ultimate performance
ShardingSphere-Proxy: Enterprise Access End
Positioning: Transparent database proxy, independently deployed server-side
Core Features:
- Static entry point: Independent deployment from applications, providing stable database access entry
- Heterogeneous language support: Supports any MySQL/PostgreSQL protocol compatible client
- DBA friendly: Database operation and maintenance management interface, convenient for O&M personnel
- Enterprise-grade features: Supports cluster deployment, load balancing, failover
Use Cases: Heterogeneous language environments, database operation and maintenance management, enterprise applications requiring unified access entry
Hybrid Architecture Advantages
By hybridizing ShardingSphere-JDBC and ShardingSphere-Proxy with unified configuration through the same registry center, you can flexibly build application systems suitable for various scenarios:
- Architectural flexibility: Architects can freely adjust the optimal system architecture
- Scenario adaptability: Select the most suitable access method according to different business scenarios
- Unified management: Single configuration, multi-end collaboration, simplifying O&M complexity
- Progressive evolution: Support smooth evolution path from JDBC to Proxy
AI ABSTRACTION
DOCUMENTATION📜
<hr>For full documentation & more details, visit: Docs
CONTRIBUTION🚀🧑💻
<hr>For guides on how to get started and setup your environment, contributor & committer guides, visit: Contribution Guidelines
Team
<hr>We deeply appreciate community contributors for their dedication to Apache ShardingSphere.
COMMUNITY & SUPPORT💝🖤
<hr>:link: Mailing List. Best for: Apache community updates, releases, changes.
:link: GitHub Issues. Best for: design discussions, bug reports, or anything development related.
:link: Slack channel. Best for: instant communications and online meetings, sharing your applications.
:link: X. Best for: keeping up to date on everything ShardingSphere.
:link: LinkedIn. Best for: professional networking and career development with other ShardingSphere contributors.
PROJECT STATUS
<hr>:white_check_mark: Version 5.5.4-SNAPSHOT: Actively under development :tada:
🔗 For the release notes, follow this link to the relevant GitHub page.
:soon: Version 5.5.4
We are currently developing version 5.5.4, which includes multiple security enhancements and performance optimizations. Keep an eye on the milestones page of this repo for the latest development progress.
TECHNICAL ARCHITECTURE EVOLUTION
<hr>Apache ShardingSphere adopts a micro-kernel + 3-layer pluggable architecture, achieving complete decoupling of the kernel, functional components, and ecosystem integration, providing developers with ultimate flexibility and extensibility.
Micro-Kernel + 3-Layer Pluggable Model
Core Layer:
- Query optimizer: Intelligent SQL routing and execution plan optimization
- Distributed transaction: ACID transaction guarantees and consistency coordination
- Execution engine: Efficient distributed execution and result aggregation
Feature Layer:
- Data sharding, readwrite-splitting, federation query
- Data encryption, data masking, SQL audit
- Shadow database, observability, traffic control
Ecosystem Layer:
- Database protocol adaptation (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, etc.)
- Registry center integration (ZooKeeper, ETCD, etc.)
- Configuration management, service discovery, monitoring integration
Technical Innovation Highlights
Complete Decoupling Architecture:
- Database types completely decoupled, supporting rapid integration of new databases
- Functional modules completely decoupled, supporting on-demand feature combination
Apache ShardingSphere consists of two access ends - JDBC and Proxy - that can be deployed independently or in hybrid deployment, providing unified distributed database solutions for diverse application scenarios including Java isomorphism, heterogeneous languages, and cloud-native environments.
ShardingSphere-JDBC
<hr>A lightweight Java framework providing extra services at the Java JDBC layer. With the client end connecting directly to the database, it provides services in the form of a jar and requires no extra deployment and dependence.
:link: For more details, follow this link to the official website.
Note: When using ShardingSphere-JDBC adapter, pay attention to your application's memory configuration. Antlr uses an internal cache to improve performance during SQL parsing. If your application has too many SQL templates, the cache will continue to grow, occupying a large amount of heap memory. According to feedback from the ANTLR official issue#4232, this issue has not yet been optimized. When connecting your application to ShardingSphere-JDBC, it is recommended to set a reasonable heap memory size using the
-Xmxparameter to avoid OOM errors caused by insufficient memory.
ShardingSphere-Proxy
<hr>A transparent database proxy, providing a database server that encapsulates the database binary protocol to support heterogeneous languages. Friendlier to DBAs, the MariaDB, MySQL and PostgreSQL version now provided can use any kind of terminal.
:link: For more details, follow this link to the official website.
Hybrid Architecture
<hr>ShardingSphere-JDBC adopts a decentralized architecture, applicable to high-performance light-weight OLTP applications developed with Java. ShardingSphere-Proxy provides static entry and all languages support, suitable for an OLAP application and sharding databases management and operation.
Through the combination of ShardingSphere-JDBC & ShardingSphere-Proxy together with a unified sharding strategy by the same registry center, the ShardingSphere ecosystem can build an application system suitable to all kinds of scenarios.
:link: More details can be found following this link to the official website.
CORE FEATURE MATRIX
<hr>Distributed Database Core Capabilities
- Data Sharding: Horizontal sharding, vertical sharding, custom sharding strategies, automatic sharding routing
- Read/Write Splitting: Master-slave replication, load balancing, failover, read weight configuration
- Distributed Transaction: XA transactions, BASE transactions, transaction propagation
Data Security & Governance
- Data Encryption: Field-level encryption, transparent encryption, key management, encryption algorithm support
- Data Masking: Sensitive data protection, masking strategy customization, dynamic masking rules
- Access Control: Fine-grained permissions, access control, SQL firewall, security policies
Database Gateway Capabilities
- Heterogeneous Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, Firebird, etc.
- SQL Dialect Translation: Cross-database SQL compatibility, dialect adaptation, syntax conversion
- Protocol Adaptation: Database protocol conversion, multi-protocol support, communication optimization
Full-link Stress Testing & Observability
- Shadow Database: Stress testing data isolation, environment separation, real data simulation
- Observability: Performance monitoring, distributed tracing, QoS analysis, metrics collection
- Traffic Analysis: SQL performance analysis, traffic statistics, bottleneck identification
Enterprise-grade Features
- High Availability: Cluster deployment, fault recovery, service discovery, health checks
- Cloud Native: Containerized deployment, Kubernetes integration, native image support
- Monitoring & Alerting: Real-time monitoring, alert notifications, performance metrics, O&M dashboard
Roadmap
<hr>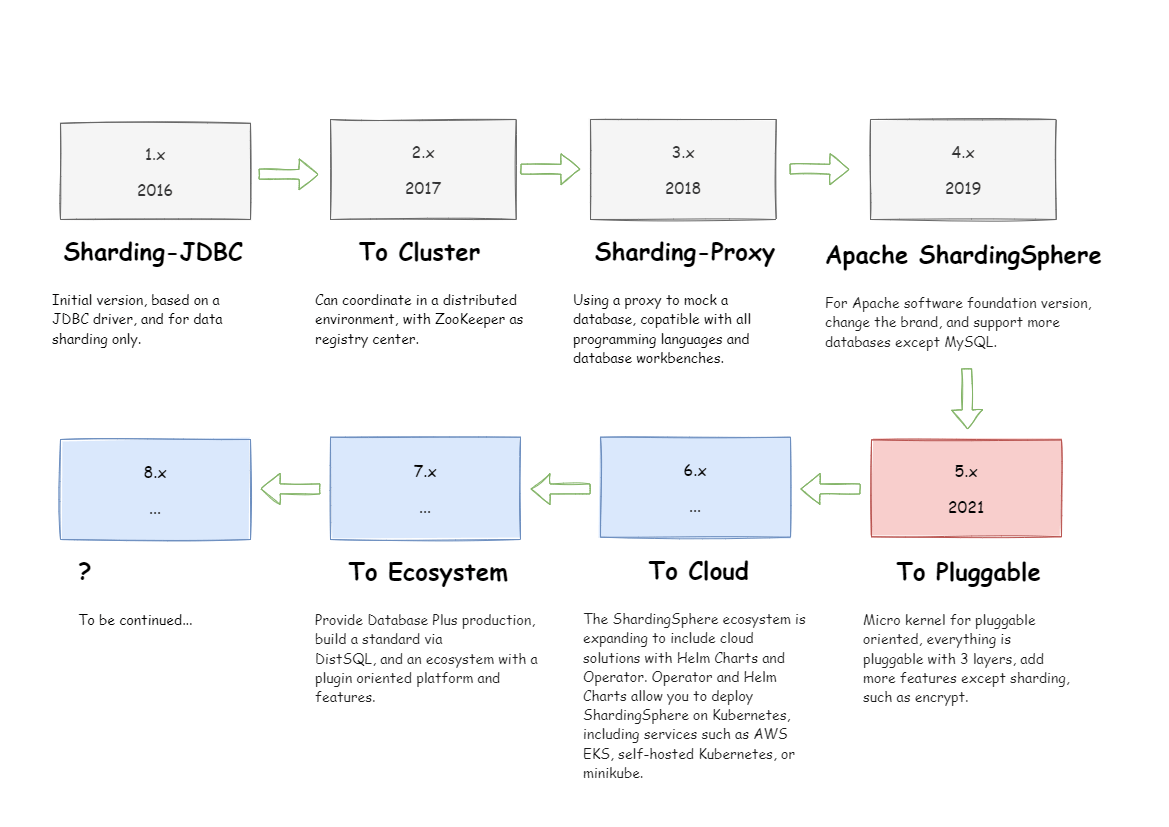
How to Build Apache ShardingSphere
<hr>Check out Wiki section for details on how to build Apache ShardingSphere and a full guide on how to get started and setup your local dev environment.










